Library receives medals, papers of Nobel laureate James Cronin
The University of Chicago Library has received the medals and academic papers of Nobel-winning physicist James Cronin, SM’53, PhD’55, the late UChicago scientist who made defining contributions to physics and astronomical observation.

James Cronin at the chalkboard.
Cronin’s children, Emily Cronin Grothe and Daniel Cronin, donated six medals that recognize his extraordinary achievements, including the 1980 Nobel Prize Medal for Physics and the 1999 National Medal of Science. His widow, Carol Cronin, donated his professional papers, including lab reports, articles, lectures, speeches, teaching materials, correspondence and other items.
The two gifts join archival collections at the Library’s Special Collections Research Center containing the papers or medals of 20 other Nobel laureates, including UChicago-associated physicists Niels Bohr, Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, Arthur H. Compton, Enrico Fermi, James Franck, Albert A. Michelson, Yoichiro Nambu and Eugene Wigner.

James Cronin’s Nobel Prize Medal.
“I am deeply grateful to the Cronin family for their invaluable gifts to the Library,” said Brenda Johnson, Library Director and University Librarian. “Making James Cronin’s papers and medals available to researchers and students not only helps us to understand the achievements of the past—it also fuels the rigorous inquiry of faculty and the transformative education we provide students. That is why the University of Chicago Library is committed to being the home of Nobel Prize winners’ research.”
Cronin earned his master’s degree and PhD in physics from UChicago in the 1950s. While conducting research in the 1960s at Brookhaven National Laboratory, he and colleague Val Fitch studied subatomic particles coming off collisions between protons and atom nuclei and found the first example of nature’s preference for matter over antimatter. It was the first observation of a mystery that had baffled scientists for decades, and the breakthrough would earn them the Nobel Prize in 1980.
This finding was later used to provide support for the Big Bang theory, explaining why the explosion would produce more matter than antimatter—leaving remnants that would eventually became stars, planets and human life.
Studying the origin of cosmic rays
Cronin joined the UChicago faculty in 1971 as University Professor of Physics. He soon shifted course to study the origin of cosmic rays: mysterious, highly energetic particles that strike the Earth from elsewhere in the cosmos. To search for them, he co-founded the Pierre Auger Observatory in Argentina—a massive international collaboration to build a system of giant water tanks spread over an area ten times the size of Paris. It took its first readings in 2005, and just last year discovered extragalactic origins for some of the cosmic rays that strike Earth.

Photo of James Cronin (left) with apparatus and colleagues.
Cronin saw himself as part of a long lineage of UChicago physicists. In 2001, he organized a symposium marking the 100th anniversary of Fermi’s birth and edited the book Fermi Remembered. Published by the University of Chicago Press in 2004, it explored the enduring significance of Fermi’s work.
“In his first year as a graduate student at the University of Chicago, Cronin studied with Enrico Fermi and developed a great respect for him,” said Daniel Meyer, director of the Special Collections Research Center. “When he was working on the Fermi centennial and publication, Cronin came to Special Collections frequently to do his own research in the Fermi papers. He examined all of Fermi’s original laboratory notebooks and located key letters and documents from Fermi’s career.”
Emily Cronin Grothe, LAB’78, said the University of Chicago Library was the right home for her father’s medals and papers.
“Our family has a long history with the University of Chicago, with my grandfather, father, mother, uncle and daughter all receiving advanced degrees from the institution,” she said. “Given that, and how proud my father was to be associated with the University and its remarkable approach and achievements in science, my brother Dan and I never wavered in our commitment to house my father’s papers and medals with The Library.”

Selected medals, awards and honors of James W. Cronin, including (left to right) the 1976 Franklin Institute John Price Wetherill Medal, the 1977 United States Department of Energy Ernest Orlando Lawrence Memorial Award Medal, the 1999 National Medal of Science, the 1999 Collège de France Service Medal, the 1980 Nobel Prize Medal for Physics, and the 1999 French Légion d’Honneur Chevalier Medal.
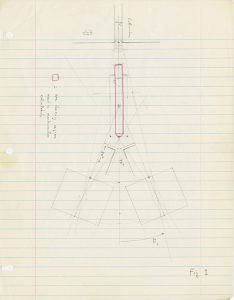
Sketches from notebook for CP experiment, JW Cronin Spring 1963.

A photograph of the apparatus used in discovery of the CP violation. A scientist is checking the electronics of the event detection system.

Notes ̴ at time of discussion of new physics ̴ 1955? Theoretical considerations on mesons and hyperons. Energy level scheme for new particles. (hyperons).

Letter from James Cronin to President Clinton, June 20, 2000, concerning the founding of the Auger Observatory. Cronin thanks Clinton for his bringing up “the international cosmic ray project during your meeting with President de la Rua of Argentina.”


